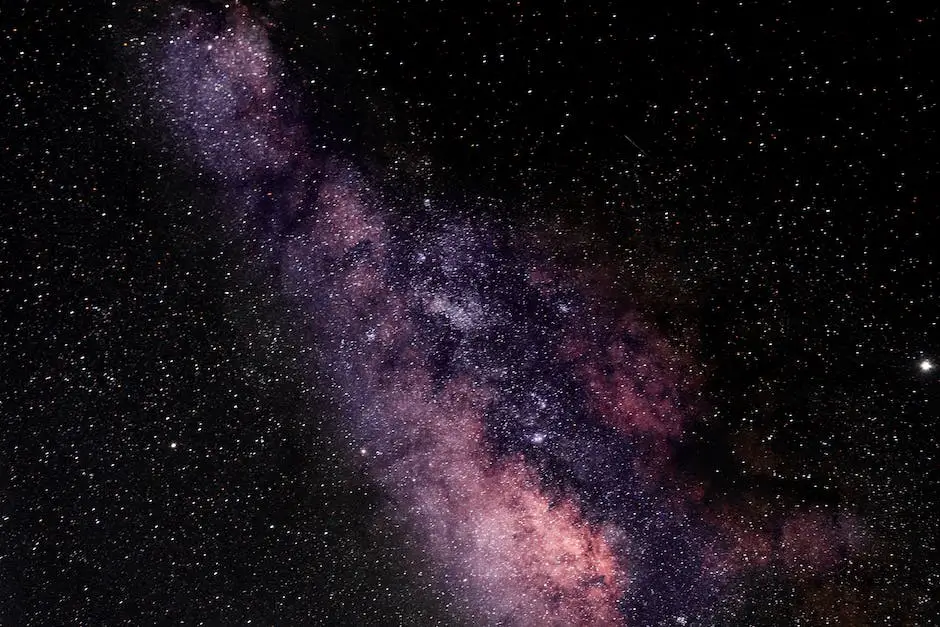
Wide angle astrophotography allows us to capture the breathtaking beauty of the night sky on a grand scale, immortalizing celestial objects and events in stunning high-resolution images. Whether you are an amateur stargazer or a seasoned astrophotographer, expanding your knowledge and skills in wide angle astrophotography can open up new creative opportunities, enabling you to capture the wonder of the cosmos in a unique and engaging way. Dive into this comprehensive guide that covers everything from equipment selection and alignment to image processing and creative photography ideas, providing you with the tools and insights to become an expert in wide angle astrophotography.
Understanding Wide Angle Astrophotography
Wide Angle Astrophotography
Wide angle astrophotography is a specialized technique within the field of astrophotography that utilizes a wide field of view to capture stunning images of celestial objects and events. This approach allows photographers to capture more of the night sky in a single image, making it especially useful for capturing large-scale astronomical phenomena such as the Milky Way, meteor showers, and aurorae. Moreover, wide angle astrophotography has the advantage of offering unique and breathtaking perspectives of familiar celestial objects that cannot be achieved through traditional astrophotography methods with a narrower field of view.
Equipment Selection
Selecting the right equipment is crucial to mastering wide angle astrophotography. Telescopes with short focal lengths are typically preferred since they can produce a wider field of view. Additionally, certain lenses, such as ultra-wide-angle or fisheye lenses, are specifically designed to provide expansive coverage of the night sky. When it comes to choosing a camera, those with larger sensors are preferable, as they can capture more light and produce higher quality images; full-frame and cropped-sensor DSLRs, as well as dedicated astronomical cameras, are all popular options among astrophotographers.
Capturing Astronomical Phenomena
Understanding the physical properties of astronomical phenomena is essential to successfully capturing them through wide angle astrophotography. For instance, the size, brightness, and apparent motion of celestial objects will all impact the final image. To capture striking images of the Milky Way, photographers must consider factors such as the orientation of the galaxy, the density of stars, and the presence of nebulae and other interstellar features. Similarly, when photographing meteor showers, knowing the peak times, radiant points, and expected meteor rates will help to determine the best strategies for capturing these fleeting events.
Optimal Conditions for Observation
Another essential element of wide angle astrophotography is the ability to take advantage of optimal conditions for celestial observation. In general, photographers should seek out dark skies free from light pollution in order to maximize the visibility of faint celestial objects. Additionally, the Moon’s phase should be taken into consideration, as a full or nearly full Moon can easily wash out faint astronomical phenomena. Photographers should also remain cognizant of atmospheric conditions, such as cloud cover and atmospheric turbulence, which can significantly impact the clarity and quality of wide angle astrophotography images.
Mastering Techniques
To excel in wide angle astrophotography, a professional must possess a strong grasp of camera settings and post-processing techniques. Capturing appropriately exposed images can be challenging due to the varying brightness levels in a night sky scene. This often involves using long exposures and high ISO settings, while being mindful of star trails and excessive digital noise. Stacking multiple images or utilizing dedicated astrophotography software can help overcome these obstacles, resulting in striking, high-quality wide angle celestial images. With practice, knowledge, and the right equipment, wide angle astrophotography can become an incredibly rewarding pursuit for both professionals and amateur photographers.

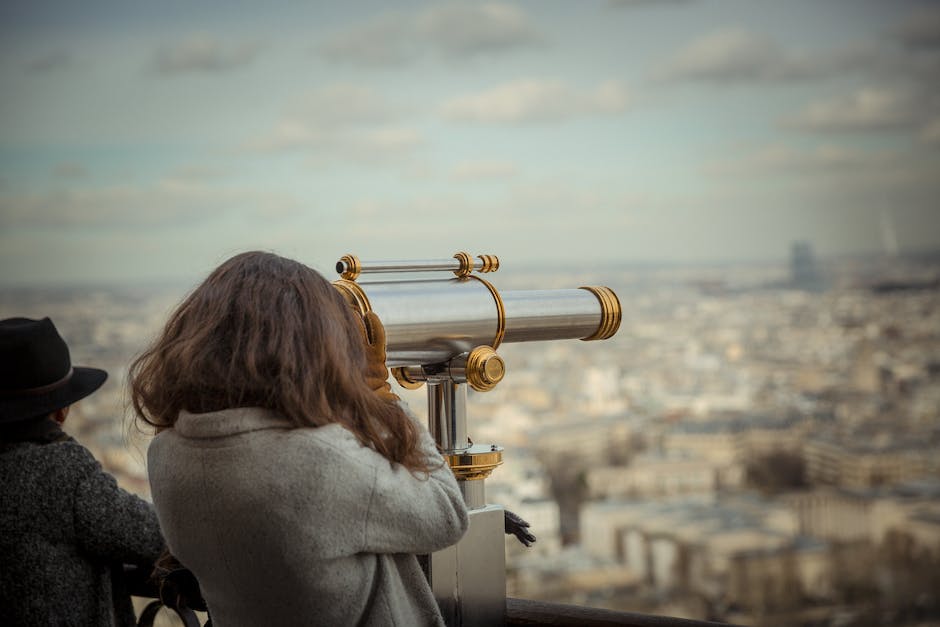
Equipment for Wide Angle Astrophotography
As a popular aspect of the broader field of astrophotography, wide angle astrophotography demands the use of specialized equipment such as telescopes, cameras, lenses, and mounts, in order to capture vast portions of the night sky with exceptional detail. Factors like budget, existing gear, and personal preferences play a significant role in determining the specific requirements and equipment selection for this specialized photography technique.
The Telescope
The first consideration for wide angle astrophotography is the telescope itself, as it serves as the foundation of the entire setup. Refractor telescopes are widely preferred for astrophotography due to their better color correction and lack of a central obstruction, which can cause diffraction spikes. A telescope with a fast focal ratio, typically f/5 or lower, will be more suitable for capturing wide-angle views of the night sky. It’s crucial to consider factors such as the size, weight, and portability of the telescope, as well as the available budget, before making a decision.
The Camera
Next, the camera plays an essential role in wide angle astrophotography, as it is responsible for capturing the light collected by the telescope. Two common types of cameras used are DSLRs and dedicated astrophotography CCD or CMOS cameras. While DSLRs can be more budget-friendly and versatile for other types of photography, dedicated astrophotography cameras offer better sensitivity and noise control, making them a preferred choice for serious enthusiasts. When selecting a camera, consider factors such as sensor size, pixel size, and the presence of a cooling system to reduce noise in the final image.
The Lens
Choosing the right lens for wide angle astrophotography can be just as important as selecting the proper telescope and camera. Prime lenses with a wide focal length, generally between 14mm and 24mm, are most suitable for capturing expansive views of the sky. A fast aperture, such as f/2.8, is ideal for allowing more light to reach the sensor and reducing exposure times. It is essential to balance factors such as optical quality, distortion, and vignetting with the available budget when choosing the right lens for this pursuit.
The Mount
Lastly, the mount is a critical component in any astrophotography setup, as it ensures accurate tracking of celestial objects and minimizes errors due to Earth’s rotation. Equatorial mounts are the preferred choice for astrophotography due to their alignment with the earth’s axis and precise tracking capabilities. For wide angle astrophotography, a lightweight and portable mount with sufficient weight capacity for the chosen telescope and camera is ideal. Higher-end mounts will offer greater accuracy and beginner-friendly features such as go-to systems that automatically locate celestial objects.
As you venture into the world of wide-angle astrophotography, assembling a high-quality setup is crucial for capturing breathtaking celestial vistas. Consider investing in accessories such as filters to enhance color detail and reduce light pollution, as well as field flatteners to eliminate field curvature. By conducting thorough research and carefully considering your preferences and budget, you’ll be able to create an effective astrophotography setup, allowing for exploration and creative expression.

Setting Up and Aligning Equipment
Once you have the right equipment, it’s vital to know how to properly assemble and align everything for stunning wide-angle astrophotography images. Begin by setting up your tripod on a flat surface, ensuring its stability, then attach the equatorial mount. Balancing the mount is essential for maintaining stability throughout your imaging sessions, especially when using heavy lenses or camera bodies. Utilize a counterweight or other balancing system if necessary to achieve optimal balance.
Next, attach the camera to the mount with a steady hand and carefully connect your wide-angle lens. Keep in mind that a good-quality, wide-field lens will provide better results than a regular lens. For wide-angle astrophotography, a focal length between 14mm and 24mm is ideal. This range will allow you to capture large areas of the night sky while still retaining the necessary detail and sharpness for captivating images. Remember to check that your camera settings are optimized for astrophotography, including shooting in RAW format, setting a wide aperture, and selecting a high ISO value.
The use of a polar alignment scope is essential for accurate tracking and precise celestial object imaging. To properly align your mount with Earth’s rotational axis, follow these steps: first, find the celestial pole in the sky (Polaris for Northern Hemisphere observers, Sigma Octantis for Southern Hemisphere observers). Then, insert the polar alignment scope into the mount’s polar axis and rotate the mount until the illuminated reticle inside the eyepiece matches the position of the celestial pole. This process will require slight adjustments to your equatorial mount’s altitude and azimuth controls to ensure that the reticle and the celestial pole perfectly align.
Verifying the accuracy of your polar alignment is crucial. One method to do this is by performing a “drift alignment” test. After the polar alignment scope process, point your camera and lens at a brightly visible star located near the celestial equator. Observe the motion of the star over a period of several minutes using a higher magnification than the typical wide-angle astrophotography setting. If the star appears to drift, adjust your mount’s altitude and azimuth controls accordingly until the drifting is minimized.
Lastly, don’t forget to fine-tune your focus to ensure sharp images. Autofocus might not work well in low-light scenarios, so it’s best to use manual focus. Try focusing on a bright star and use live view on your camera to check its sharpness. Many cameras offer a built-in focus magnifier or a focusing aid to help you achieve the best focus possible. Keep an eye on your focus throughout the imaging session, as temperature changes can sometimes cause it to shift, requiring minor adjustments to maintain optimal sharpness.

Astrophotography Techniques and Tips
Moving on to wide angle astrophotography, this exciting and accessible technique allows photographers to capture breathtaking images of the cosmos, encompassing vast expanses of the sky within a single frame. A common method employed in this field is long exposure, which involves keeping the camera’s shutter open for an extended period to gather as much light as possible, a crucial element for capturing the faint light of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. However, long exposures may also result in star trails due to the Earth’s rotation, making the balance between exposure time and the desired level of detail extremely important.
Stacking is another widely used technique in wide angle astrophotography, which involves taking multiple images of the same area of the sky and then combining them using specialized software. This process helps to reduce noise, increase detail, and improve the overall quality of the resulting image. It’s crucial to use a tripod and a remote shutter release or intervalometer to ensure that the separate frames are aligned perfectly when stacking.
Tracking is an advanced technique used to counteract the Earth’s rotation, enabling photographers to take longer exposures without creating star trails. This involves using an equatorial mount or a star tracker, which follows the movement of the sky, allowing the camera to remain fixed on the celestial objects. While this method may be more complex and require additional equipment, it can yield impressive results, especially when capturing deep-sky objects like galaxies and nebulae.
Focusing and framing are essential skills for wide angle astrophotography, and getting both of these elements right can greatly impact the quality of the final image. To ensure the stars are sharply focused, switch to manual focus and use the camera’s live view function, zooming in on a bright star to make adjustments. Framing the shot includes experimenting with different compositions, positioning the camera to incorporate interesting foreground elements or finding the best balance between sky and land.
Lastly, achieving successful wide angle astrophotography requires a thorough understanding of the impact of light pollution. Light pollution significantly reduces the visibility of stars and other celestial objects, making it important to find dark sky locations away from city lights. By choosing the right camera settings, such as using a lower ISO to reduce noise and ensuring appropriate camera exposure, photographers can minimize the effects of light pollution. Additionally, utilizing various filters designed to block specific wavelengths of artificial light can further improve image quality. Taking these factors into account, photographers can optimize their chances of capturing stunning wide angle astrophotography images.
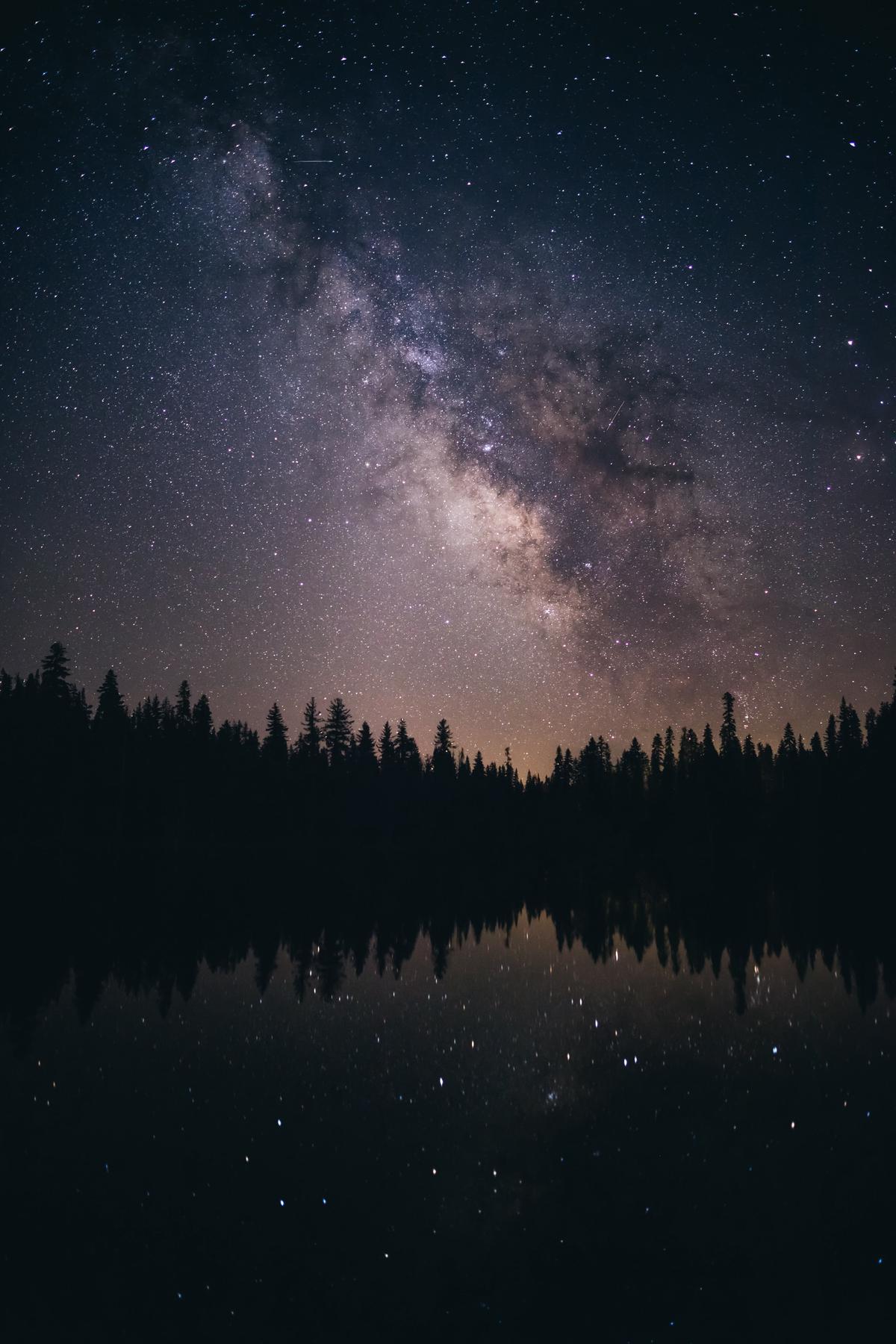

Processing and Editing Astrophotography Images
After capturing these images, processing and editing them is essential in order to create vibrant, high-quality final results that truly showcase the beauty and grandeur of the night sky. In wide angle astrophotography, various post-processing techniques and software tools are employed to enhance the final image. Some of these techniques include stacking, noise reduction, and adjusting curves and levels. By effectively implementing these enhancements, photographers can further refine their wide angle astrophotography skills and produce captivating images of the night sky.
To achieve the best results in wide angle astrophotography, image stacking is a commonly employed technique. Through this process, a series of individual exposures are combined to create a single image with increased detail and reduced noise. This is particularly important in astrophotography, as the increased signal-to-noise ratio allows for the capturing of faint celestial objects and structures that may be difficult to discern in a single exposure. There are many software options available for stacking, such as DeepSkyStacker and Sequator, which cater specifically to this aspect of astrophotography.
Another important consideration in processing astrophotography images is noise reduction. The long exposure times and high ISO settings often required for wide angle astrophotography can introduce unwanted digital noise and artifacts into the final image. To counteract this issue, dedicated noise reduction software, such as Topaz DeNoise AI or Neat Image, can be used to intelligently remove noise while preserving important details. Noise reduction can also be accomplished to some extent through in-camera settings, such as long exposure noise reduction or dark frame subtraction.
Adjusting curves and levels is another essential step in processing wide angle astrophotography images. This technique is used to optimize the brightness and contrast of the image, revealing faint details and color that might otherwise go unnoticed. Histogram adjustment can be particularly helpful in this regard, as it allows for precise control over the tonal range of the image. Programs like Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, and PixInsight offer powerful tools for making these adjustments, providing photographers with the ability to fine-tune their images to their desired aesthetic.
Wide angle astrophotography is a growing trend that allows photographers to capture the beauty and splendor of the night sky in breathtaking detail. As more enthusiasts explore this captivating form of photography, it is essential to learn the key steps involved in processing and editing images to achieve their full potential. Detailed tutorials and specialized software enable both experienced and novice astrophotographers to unlock the magic of their shots, turning a simple photograph into a cosmic masterpiece.

Creative Wide Angle Astrophotography Ideas
Techniques for Wide Angle Astrophotography
One creative technique in wide angle astrophotography is to incorporate landscape elements, using the foreground to add depth and context to your images. By framing your shot with natural landmarks such as mountains or trees, you can create a stunning contrast against the starry sky. This approach not only showcases the vastness of the universe but also emphasizes the timeless beauty of our planet. Mastering tools and techniques such as image stacking, noise reduction, and adjusting curves and levels is paramount to transforming your raw, unprocessed image into an awe-inspiring work of art.
Including Human Subjects
Including human subjects in your wide angle astrophotography can add a personal touch to your images while also providing a sense of scale. Place a person in the foreground, perhaps engaging in an activity like stargazing or simply gazing up at the Milky Way, to create a connection with the viewer. Experiment with various poses and compositions to find the perfect balance between the vastness of the sky and the human presence. This technique can evoke powerful emotions and spark curiosity about our place in the cosmos.
Time-lapse Videos
Time-lapse videos are another exciting and creative approach to wide angle astrophotography. By capturing a series of images over an extended period, you can create a dynamic visual representation of celestial events, such as the motion of the stars, the phases of the moon, or even the slow crawl of the Milky Way across the sky. This technique can also be used to highlight changes in the landscape or weather during the transition from day to night, or vice versa. Time-lapse videos combine the beauty of still photography with the engaging nature of video, allowing you to tell a unique and captivating story with your images.
Post-Processing Techniques
An additional innovative idea is to experiment with different techniques for post-processing your images, such as stacking, which involves layering multiple exposures to create a single, high-quality image. This can help to bring out the faint details in the night sky that may not be visible in a single exposure, allowing you to create more impactful and visually stunning images. Another option is to play with color grading and adjustments in post-processing to enhance the natural colors of the sky and create a striking and surreal effect.
Light Painting
Combining wide angle astrophotography with light painting can also result in some fascinating and imaginative images. By using a flashlight, headlamp, or other light source to illuminate your foreground subjects during a long exposure, you can create vibrant and colorful scenes that contrast beautifully with the night sky. Light painting can be used to highlight interesting elements in your landscape or to create dynamic human silhouettes that add an engaging and interactive element to your photographs. Embracing creative and innovative ideas like these can help you take your wide angle astrophotography skills to new heights, capturing the beauty of the universe in a truly unique and captivating manner.

Throughout this guide, we have explored the captivating world of wide angle astrophotography and its many facets, covering equipment, techniques, and creative ideas. Armed with this knowledge, you are now ready to embark on your own journey to create awe-inspiring celestial images that capture the vastness and beauty of the cosmos. Embrace the challenges and rewards of wide angle astrophotography, harnessing the power of the night sky to produce unforgettable imagery and inspiring others to appreciate the wonders of the universe that surround us.
Originally posted 2023-05-25 18:11:20.